Definition of Volcano
The volcano : is a geological structure resulting from the rise and accumulation on the surface of magmatic material molten lava. Their shape, somewhat flattened and / or rounded, the result of greater or lesser viscosity lavas concerned.
A volcano eruption in early:
Erupting Volcano :
Fumaroles of the volcano shows activity that could lead to an eruption. A volcano is an opening, or rupture, in a planet's surface or its bark, which allows hot magma, volcanic ash and gases to escape from the magma chamber beneath the surface.
Most volcanic rocks are basic and give birth with decomposition at very fertile soils. Volcanic rocks are commonly used in aquariums to form the hardscape. Pozzolan is a material derived from crushed volcanic rock.
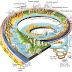
A volcano is the place of the earth's crust where the magma and gases reach the surface. Depending on the nature of the emitted lava, volcanic apparatus take different forms. Thus was distinguished for very long volcanoes:
- Hawaiians type characterized by cone gentle slopes (4-6) to several tens of kilometers formed by stacking fluid basaltic lava flows very;
-Strombolian volcanoes (Stromboli, Italy) made a pointed cone formed by alternating lava flows and pyroclastic materials (projection of various materials: blocks, lapilli, ash);
-Vulcan type of volcanoes (Vulcano in Italy), the cone is formed only from the accumulation of projections;
-Pelean type volcanoes (Mount Pelee in Martinique), characterized by lava highly viscous which do not flow and form needles that are sprayed on the occasion by gases that pressure below (phenomenon of glowing cloud) .
This classification of volcanic devices do not reflect the diversity of eruptions that depends on several characteristics of lava. Thus one can know the volcano during its different phases of activity, rashes characterize one or another type of volcanic unit.
The submarine volcanism and volcanism in continental rifts (East Africa) do not fit into any of these categories when it is the most important. The submarine volcanism is characterized by fissure eruptions, the lava never goes to the same place and by fluid lava flows forming, because of the rapid cooling and the hydrostatic pressure of the particular structures, lava pillows.
Erupting volcanoes can pose many dangers, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. Volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, particularly those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid clears the air, and can cool the lower atmosphere of the Earth or the troposphere, but they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, warming the stratosphere. Historically, the so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.











No comments
Post a Comment